
Trunk links have a special VLAN called the Native VLAN. This is recommended for security reasons. If desired, the list of VLANs allowed on the trunk can be restricted to a specific list. For this reason, trunking is also known as tagging. This is done by adding an 802.1Q tag in the Ethernet frame header. Their purpose is to carry traffic for multiple VLANs. In this case, a special Voice VLAN is added to the port.Ī trunk port is used when connecting switches together. We also connect phones to access ports, and workstations to the phones. The access port is configured with a single VLAN. Layer-2 interfaces can be configured as access ports or trunk ports.Īccess ports are where we connect endpoints, like workstations, printers, and some servers. This uses a client/server model, where server switches give client switches a list of VLANs that they need to add.įor practical purposes, it’s recommended to disable VTP (set it to transparent mode). It’s a protocol on Cisco switches that makes it easier to configure VLANs across many switches. VTP is a technology that you may see in the real world. NOTE: VTP is not in the current CCNA exam. VLAN 1 is the default VLAN on Cisco switches. They also break VLANs into two ranges (1-1001 is the normal range, 1006-4094 is the extended range). Cisco reserve a few VLANs for special purposes. There are many reasons to use VLANs, including security, traffic separation, and organization. Think of this like mini-virtual switches. VLANs are used to divide the network into logical parts. Some is broadcast (sent to all endpoints in the network segment), or multicast (sent to some endpoints). Most traffic is unicast (sent to one specific destination). If entries in the MAC address table are not refreshed, they age out, meaning that they are removed from the table. If a MAC is not in the table, the frame is flooded, and positive results are recorded. The switch consults the MAC address table when it needs to forward a frame. These are stored in the MAC address table, along with the best interface to reach it. To do this, switches learn MAC addresses of devices in the network segment. That is, the router updates the source MAC as it’s own, and the destination MAC as the next-hop.įrame switching is the switches ability to find the right layer-2 path, and send a frame across it. When frames are sent through the network, they are rewritten by layer-3 devices. At layer-2, they primarily work with Ethernet frames and MAC addresses. If there are no ARP entries on the switch then it is a sign that the switch management interface has not been used to access other IP addresses.Switches traditionally operate at layer-2, although many are capable of layer-3 (routing) functions as well. Remembering that the ARP table is the result of routing activity we can understand that if you have used the management interface of the switch to access network resources within its own subnet (ping in its own subnet is a good example) there there would be entries in the ARP table of the switch. The switch will certainly have a mac address table and it may have an ARP table. It may be that you need to session to the switch to see its mac address table. But you may not be able to see the switch mac address table from the router command line. If your router has a switch module then the switch module will build a MAC address table. So the MAC address table is the result of switching activity and the ARP table is the result of routing activity. The MAC address table is the result of layer 2 activity and is built as layer 2 interfaces receive a frame and discover the source MAC address of the frame. The ARP table is the result of layer 3 activity and is built as layer 3 interfaces look for and find the MAC address associated with an IP address. To answer this let us start by understanding the 2 things (ARP table, and MAC address table) and how they are used and how they are different. What is wrong with this? Is it because of GNS3?

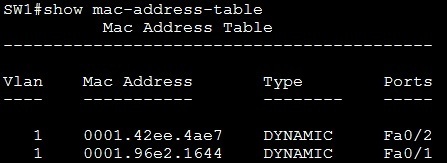
But I can't see mac-address-table from router and arp table from switch. Question) So, when I do "show ?" i can see both "arp" and "mac-address-table" supported from both router and switch. Internet 1.1.1.2 - 0000.0000.0002 ARPA FastEthernet0/0įrom switch, show mac-address-table shows all output, but "show arp"ĭestination Address Address Type VLAN Destination Port Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface For switch, I am attaching switch 16 module for simulation.įor my router and switch (router with switch module on it) both works commands "show arp" and "show mac-address-table".įrom router, "show arp" shows all output, but when I use "show mac-address-table" it doesn't show any output.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
